break function
Used to set a breakpoint at the sourceline or the function. In the case of the sourceline, execution is stopped before any code on the line is executed. In the case of the function, execution stops when the function is entered.
Start execution of the program. If breakpoints are set, execution stops when the sourceline or function is reached. Otherwise, the program runs to completion. gdb prints a message stating the status of the program on termination.
Continue execution from where it stopped.
Kill execution of the program begin run. Typically used to prepare to re-start the program from the beginning.
step [n]
Execute the next or next n source line(s). This command steps into functions.
next [n]
Same as step, but the command steps past functions, treating them as if they were single statements.
- delete
Deletes all breakpoints
- clear sourceline
clear functionDeletes any breakpoints set on the sourceline or at the entry of function.
Print a backtrace of all the active functions on the stack. This is very useful in determining the order in which functions call each other.
Print the value of expression. The contents of variables in the program can be viewed through this command.
- print i
Print the value of variable i. - print *p
Print the contents of memory pointed to by p, where p is a pointer variable. - print x.field
Check the different members of a structure. - print x
Check all the members of a structure, assuming x is a structure. - print y-
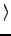 field
field
y is a pointer to a structure. - print array[i]
Print the i'th element of array. - print array
Print all the elements of array.
list sourcefile:sourceline
list function
list
Print 10 lines centered at sourceline or starting from the beginning of function. By itself, print 10 more lines.
Display the set of commands available in gdb.
Exit gdb.