Decoders, Encoders, and Muxes, Oh My!
Tom Kelliher, CS 240
Feb. 18, 2008
Read 4.1-4.2. Review mostly; background for carry lookahead.
Combinational design example.
- Decoders
- Encoders
- Muxes
Lower bound for addition. Fast addition algorithms.
Block diagram (diagram a 3-8 decoder):
A circuit with 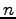 inputs. The inputs are interpreted as a binary number
and used to select one of
inputs. The inputs are interpreted as a binary number
and used to select one of 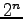 output lines.
output lines.
- Most common use: Address decoders for RAMs and register files.
- Decoder expansion example: design a 5-to-32 using 5 3-to-8 decoders.
- Example use: Design a BCD to seven segment decoder using a 4 to 16
decoder and OR gates.
Inverse of a decoder: 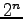 inputs;
inputs; 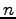 outputs.
outputs.
- What happens if multiple inputs are high?
- Most common uses: priority encoders for interrupt controllers;
``hit'' logic for caches.
- Design example: Four input priority encoder with a ``Valid'' output.
Used to select one of 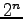 inputs. One way switch.
inputs. One way switch.
Block diagram (draw a 4-1 mux):
- Most common uses: RAM, register file data selection circuits; Boolean
function generators.
- What's a quad 2-1 mux?
- Design example: Implement a three input Boolean function using an 8-1
mux. No additional logic.
Four input Boolean function using an 8-1 mux and an inverter?
Five input Boolean function?
Thomas P. Kelliher
2008-02-14
Tom Kelliher
![\begin{figure}\centering\includegraphics[]{Figures/decoder.eps}\end{figure}](feb18img1.png)
![\begin{figure}\centering\includegraphics[]{Figures/decoder.eps}\end{figure}](feb18img1.png)
![]() inputs. The inputs are interpreted as a binary number
and used to select one of
inputs. The inputs are interpreted as a binary number
and used to select one of ![]() output lines.
output lines.
![]() inputs;
inputs; ![]() outputs.
outputs.
![]() inputs. One way switch.
inputs. One way switch.
![\begin{figure}\centering\includegraphics[]{Figures/mux.eps}\end{figure}](feb18img4.png)