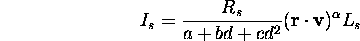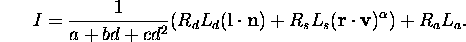More Light on Light
Tom Kelliher, CS 320
Apr. 11, 2003
Projects due Wednesday.
Read Chapter 6.
Introduction to light.
- Derivation of Phong lighting model.
- Computing normal vectors.
Project day.
- Consider an object point,
 and a light source
and a light source  .
.
- Important vectors:
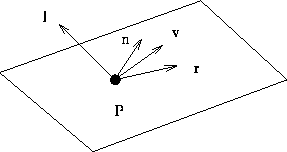
- l: vector to light source.
- n: surface normal.
- v: vector to COP.
- r: reflection vector.
- The light from source to object can be described by:
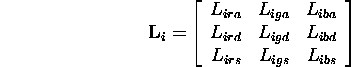
(theoretically wrong but, in practice, right)
- Using material properties, distance from source, orientation of
surface and direction of source a reflection matrix can be constructed:
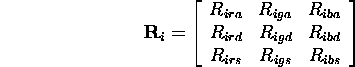
- (Simplified) Illumination at
 :
:
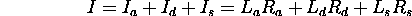
A global ambient term may be ``thrown'' in.
Same at each point on a surface:

Repeat for each color.
- Diffuse surface brightest at noon, dimmest at dawn, dusk.
- Lambert's law: we see only the vertical component of light:

- If
 and
and  are normalized:
are normalized:

So:
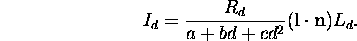
- Specular reflection produces highlights.
- The smoother the surface (higher shininess) the narrower the range
of reflection angles.
- Reflectivity proportional to angle between viewer (
 ) and
perfect reflection (
) and
perfect reflection ( ):
):

where  is the shininess term:
is the shininess term:
- < 100 for objects with broad highlights.
- 100 to 500 for most metallic objects.
- Assuming normalized vectors:
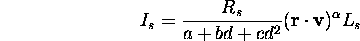
Computed for each light source and each color:
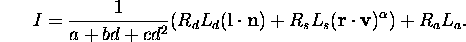
- Outward facing normal must be specified for each vertex.
- Analytic surfaces: cross product of partial differentials
- Polygonal surfaces:
- Points of continuity.
- Points of discontinuity.
Thomas P. Kelliher
Wed Apr 9 11:15:12 EDT 2003
Tom Kelliher
 and a light source
and a light source  .
.

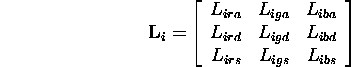
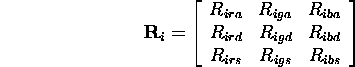
 :
:
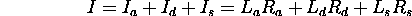
 and a light source
and a light source  .
.

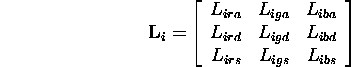
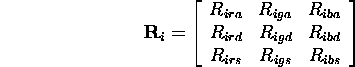
 :
:
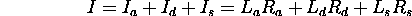


 and
and  are normalized:
are normalized:

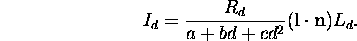
 ) and
perfect reflection (
) and
perfect reflection ( ):
):

 is the shininess term:
is the shininess term: