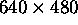 ,
, 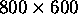 ,
, 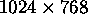 ,
etc.
,
etc.
Aspect ratio.
Tom Kelliher, CS 320
Jan. 24, 2001
C, OpenGL intros.
Programmer's API and CG architectures.
Real physics: lots of compute cycles (slow), accurate.
AGP bus and main memory ``stealing.''
A plus if graphics sub-system is designed so that applications can be written in a device-independent way.
Frame buffer attributes:
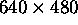 ,
, 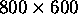 ,
, 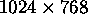 ,
etc.
,
etc.
Aspect ratio.
Object exists independently.
Its image is dependent upon view and other things such as light.
Visual acuity: resolution.
Three types of cones, each most sensitive to a particular light frequency (blue, green, yellow).
Response is non-linear for one type of cone and non-uniform between cones.
Consider the project of an object of height h onto the focal plane of a pinhole camera:
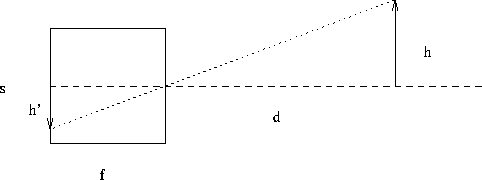
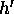 )?
)?