Introduction
Tom Kelliher, CS 320
Jan. 28, 2000
Fourth and Pixels reading.
(Repeat) Chapters 1 and 2.
Terminology.
- Graphics system architecture, CRT structure.
- Graphics: a synthetic world.
OpenGL programming.
Overall architecture:
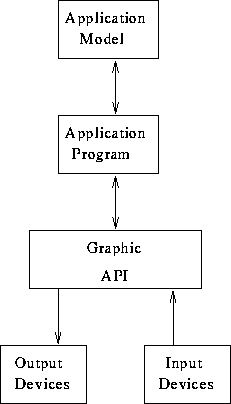
Hardware components:
- Processor.
- Memory.
- Frame buffer.
- Input, output devices.
Monochrome:
- Electron Gun.
- Focus.
- X-, y-deflection coils.
- phosphor.
Multiple intensities available.
Color:
- Electron gun s: R, G, B.
- Shadow mask.
- Triads on the phosphor.
- Color mixing: intensity.
- Additive effects of RGB.
- Monitors are analog, but frame buffers are digital. ``True color.''
Here, we take a high-level view of computer graphics.
Name two necessary components for image formation:
- Object.
- Viewer.
Is an image an object? Why or why not?
Are object and viewer sufficient? What about light? How do we model
light?
Simplifications:
- Point light sources. How good a model? Properties of light sources:
- Position.
- Intensity.
- Color.
- Directionality.
- Monochromatic light. Not a restriction, due to additive properties
of light.
Rays radiate from light sources in all directions. They can:
- Travel directly to viewer.
- Travel to infinity, not being viewed.
- Reflect from object and travel to viewer.
- Pass through object and travel to viewer.
- Interact with several objects before traveling to viewer.
- Etc.
Material properties of object:
- Transparent/Opaque.
- Reflect/Diffuse.
- Refract.
Ray tracing is a scene illuminating technique based on these ideas.
A problem: the computational complexity.
Parts of the eye:
- Cornea.
- Iris.
- Lens.
- Rods and cones.
- Retina.
What determines the visual resolution of our eyes?
What parts does the lens play?
Three types of cones, sensitive to different light frequencies:
- Blue --- less sensitivity.
- Green.
- Yellow (red).
Properties of a pinhole camera:
- A perfect pinhole: only one ray from each point passes through the
pinhole. Yields infinite depth of field.
- Depth.
- Width and height of the film.
Compute the projection of a point onto the film.
Compute the field of view.
What are the advantages/disadvantages of a lens?
Based on our pinhole camera, the model used in computer graphics.
Properties:
- Lens
- Bellows, allowing depth adjustment.
- Width and height of the film.
Development:
- Projection on the film plane may be ``reflected out front.'' This is
called the projection plane.
- Center of projection: center of lens.
- Image on the projection plane consists of all points visible and in
field of view of center of projection.
- A clipping rectangle may be used to reduce the field of view.
Thomas P. Kelliher
Thu Jan 27 12:50:16 EST 2000
Tom Kelliher

