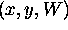 .
.
Tom Kelliher, CS 320
Apr. 26, 2000
Evaluations Friday.
Lab day Friday.
cube.c
Lab day.
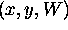 .
.
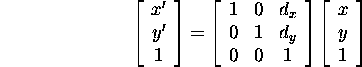
A scaling:
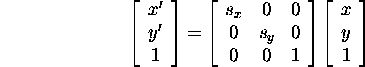
A rotation:
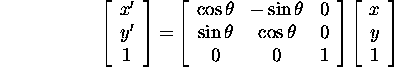
Recall:
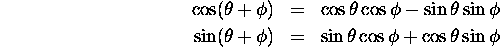
Can we combine transformations?
 ,
,  and
and
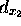 ,
, 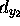 .
.
Consider the x-shear transformation:


So, a point, v, ``sees'' the transformation:

If I want to apply the transformations 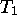 ,
, 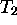 , and
, and 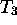 , in what
order do I perform the modelview multiplications?
, in what
order do I perform the modelview multiplications?