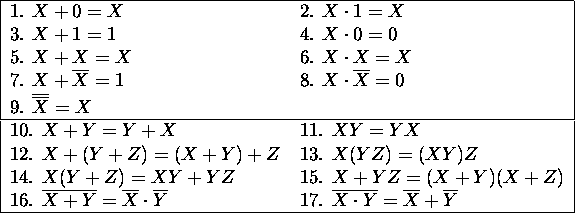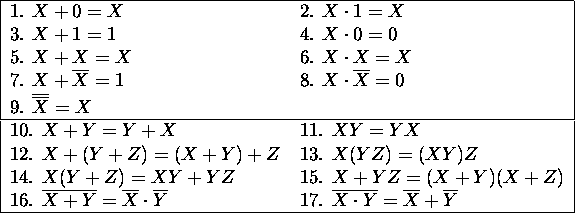Binary Logic, Gates, and Boolean Algebra
Tom Kelliher, CS 220
Sept. 12, 2003
Read 2.3--4. Written assignment due 9/19.
Radix conversions, characters codes, parity.
- Binary logic and Gates.
- Boolean Algebra.
Standard forms, maps, and minimization.
- Fundamental operators and their symbols:
- AND
- OR
- NOT
- NAND is complete.
- Gate fan-in and fan-out. Electrical significance.
- Timing diagram.
- Frequency and period.
- Timing diagrams. Show AND, OR, NOT waveforms for input: A: 0011,
B: 0101.
- What do the waveforms really look like: propagation delay, noise,
under- and over-shoot.
- Boolean functions can be represented by equations, truth tables, or
logic circuits.
How do you convert from one form to another?
How many rows in the truth table of an n-input Boolean function?
- Why would we want to simplify a Boolean equation?
- Basic Identities:
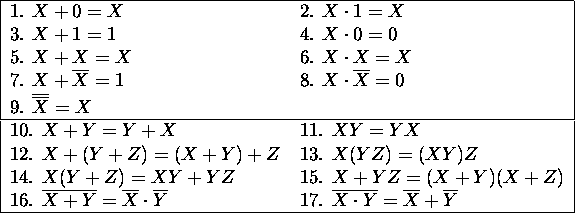
Example simplification. Use Boolean manipulation to show: 
Begin the homework problems.
Thomas P. Kelliher
Wed Sep 10 10:52:46 EDT 2003
Tom Kelliher