Tom Kelliher, CS 220
Sept. 7, 2001
Study binary, hex addition/subtraction on your own. Responsible for assigned readings.
Read 2.1--2.
Binary logic, gates, Boolean algebra.

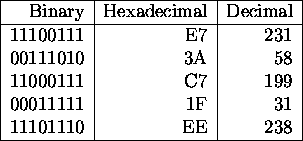
Binary or hexadecimal to decimal is simple enough.
Decimal to binary algorithm:
/* d: decimal number
* b: binary number
* b[i]: bit i of b
*/
b = 0;
i = 0;
while (d != 0)
{
b[i] = d % 2; /* d modulo 2 (radix) */
d = d / 2; /* Integer division */
++i;
}
Example: convert 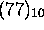 to binary.
to binary.
How do we modify this for hexadecimal? Repeat the example.
Collating sequence.
C code to convert an integer numeric string to integer value:
char s[] = "123";
int val;
int i;
val = 0;
i = 0;
while (isdigit(s[i])
{
val = val * 10;
val = s[i] - '0';
++i;
}
What about characters for non-English languages, math characters, etc? Unicode: 16-bit character code.
Detects single bit errors. Misses double bit errors.
Odd parity examples: 0011010 becomes 00011010; 0110011 becomes 10110011.