Applets and Methods
Tom Kelliher, CS 116
Sept. 11, 2000
Read Section 2.3.
Lab recap, intro. to applets.
- Methods: declarations, parameters, inheritance, overriding. Calling.
- Comments.
-
Add class example.
2-D graphics programming in Java.
Continued from last time:
-
method declaration:
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
// ...
}
- Meanings? Parameters, return value.
- The signature never changes.
- Method declaration, formal parameters.
- Inheritance and Overriding.
We will nearly always override paint(), which is defined in the
Component class:
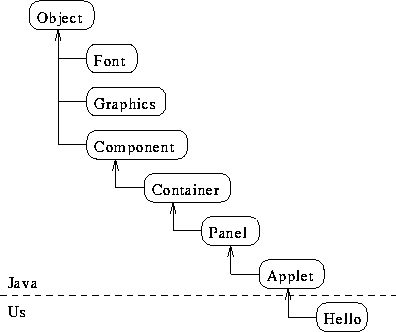
Working up the class hierarchy to find a method definition.
- Calling an object's method:
g.drawString("Hello, world!", 20, 10);
- General form:
returnValue = objectName.methodName(parameter list);
// "Parameter" is a synonym for "argument."
- Comments:
Purpose of comments. Ways to lessen the need for comments.
- What does every applet require, in terms of statements, declarations?
- What must a statement end with?
- How is a class delimited? A method?
Purpose of an applet's paint() and init() methods, within the
context of MS Windows.
Apply this to
Colors.java.
Observe:
- Adds two numbers, displaying sum.
- Documentation conventions.
- Instance, local variables.
-
init() method vs. paint() method.
- String concatenation in
drawString().
- The
add() method:
- Definition vs. call.
- Formal vs. actual parameters.
//======================================================================
// Project: CS 116, applet demo
// Author: Tom Kelliher
// File: Add.java
// Purpose: To further demonstrate some simple properties of
// applets.
//======================================================================
import java.applet.*;
import java.awt.*;
//======================================================================
// Class: add
// Purpose: Display the sum of two integers.
//======================================================================
public class Add extends Applet
{
int augend = -45;
int addend = 34;
Font f = new Font("Helvetica",Font.BOLD,18);
//===================================================================
// Method: init
// Purpose: Set background color.
//===================================================================
public void init()
{
setBackground(Color.blue);
}
//===================================================================
// Method: paint
// Purpose: Set foreground color and font.
// Display the sum string.
// Input: A graphics object.
//===================================================================
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
int sum;
sum = add(augend, addend);
g.setColor(Color.yellow);
g.setFont(f);
g.drawString(augend + " + " + addend + " = " + sum, 50, 50);
}
//===================================================================
// Method: add
// Purpose: Add two integers, returning their value.
// Input: Two integers.
// Output: Returns the sum of the integer.
//===================================================================
public int add(int a, int b)
{
int s; // The sum.
s = a + b;
return s;
}
}
Run
the applet.
Thomas P. Kelliher
Fri Sep 8 09:20:19 EDT 2000
Tom Kelliher
