CPU Scheduling
Tom Kelliher, CS42
Sept. 25, 1996
- Multi-level queues --- prioritized set of queues,
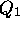 to
to  .
.
- Processes in queue i always have priority over queues >
i.
- A process remains within the same queue.
- Each queue may have its own scheduling algorithm.
- Alternative: each queue gets some fixed slice of the total CPU
cycles.
- Example: Queue for interactive jobs, RR scheduling; queue for
batch jobs, FCFS.
- Multi-level feedback queues --- similar to multi-level queues, except
that a process can move between different queues, based upon CPU usage.
- Must specify rules for moving the processes between queues.
- Ordinarily, lower priority queues have greater quantums, etc.
- Unix uses this method, with a 100ms quantum for all
queues. 128 priorities, with 32 queues.
Suppose the following jobs arrive for processing at the times indicated and
run with the specified CPU bursts (at the end of a burst a process waits
for one time unit on a resource). Assume that a just-created job enters
the ready queue after any job entering the ready queue from the wait queue.
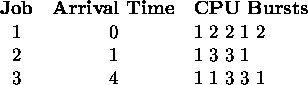
Calculate the average turnaround time for each of the scheduling
disciplines listed:
- First Come First Served.
- Shortest Remaining Time (assume that the running time
is the sum of the CPU bursts).
- Round robin with a quantum of 1.
Don't forget the ``bubble'' cycles (where no process is runnable), if
required.
Recall cooperating processes --- they affect or are affected by
other processes through access to shared variables.
E.g., threads.
Producer/Consumer (again).
const int N = 10;
int in = 0, out = 0, count = 0;
data buffer[N];
producer()
{
data next;
while (1)
{
produce in next;
while (counter == n)
;
buffer[in] = next;
in = ++in % N;
++counter;
}
}
consumer()
{
data next;
while (1)
{
while (counter == 0)
;
next = buffer[out];
out = ++out % N;
--counter;
consume next;
}
}
What variables are being shared?
What is the nature of the sharing?
- For getting shared access to resources (variables, buffers, devices,
etc.).
Critical variables; critical sections.
- For communicating.
Cases where cooperating processes need not synchronize to share resources:
- All processes are read only.
- All processes are write only (CRT screen).
- One process writes (atomically), all other processes read.
What does atomic mean?
Characteristics of ``trouble situations:''
- Multiple processes doing updates non-atomically.
- Non-atomic write processes coupled with read or update processes
The overlapping portion of each process, where the shared variables
are being accessed.
Necessary conditions for a solution to the c.s. problem:
- Mutual Exclusion --- if
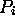 is executing in one of its critical
sections, no
is executing in one of its critical
sections, no 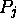 ,
, 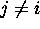 , is executing in its critical sections.
, is executing in its critical sections.
- Progress --- a process operating outside of its critical section
cannot prevent other processes from entering theirs; processes attempting
to enter their critical sections simultaneously must decide which process
enters eventually.
- Bounded Waiting --- a process attempting to enter its critical
region will be able to do so eventually.
Assumptions:
- No assumptions made about relative speed of processes
- No process may remain in its critical section indefinitely (may not
terminate in its critical section)
- A memory operation (read or write) is atomic --- cannot be
interrupted. For now, we do not assume indivisible RMW cycles.
(for n processes, 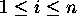 )
)
Pi:
do {
mutexbegin; /* CS entry */
CSi;
mutexend; /* CS exit */
non-CS
} while (!done);
FAI solution to CS problem for n processes:
int nextTicket = 0, serving = 0;
mutexbegin()
{
int myTicket;
myTicket = FAI(nextTicket);
while (myTicket != serving)
;
}
mutexend()
{
++serving;
}
Correctness proof:
- Mutual exclusion: contradiction.
Assumption: no process ``plays'' with control variables.
- Progress: by inspection, there's no involvement from processes
operating outside their CSs.
- Bounded waiting: myTicket at most n more than
serving.
Thomas P. Kelliher
Mon Sep 23 22:04:04 EDT 1996
Tom Kelliher
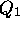 to
to 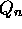 .
.
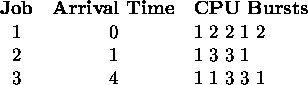
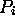 is executing in one of its critical
sections, no
is executing in one of its critical
sections, no 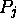 ,
, 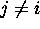 , is executing in its critical sections.
, is executing in its critical sections.
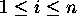 )
)