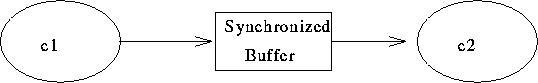Operating System Components and Services
Tom Kelliher, CS42
Sept. 10, 1996
From the virtual machine point of view (also resource management)
These components reflect the services made available by the O.S.
- Process Management
- Process is a program in execution --- numerous processes to choose
from in a multiprogrammed system,
- Process creation/deletion (bookkeeping)
- Process suspension/resumption (scheduling, system vs. user)
- Process synchronization
- Process communication
- Deadlock handling
- Memory Management
- Maintain bookkeeping information
- Map processes to memory locations
- Allocate/deallocate memory space as requested/required
- I/O Device Management
- Disk management functions such as free space management, storage
allocation, fragmentation removal, head scheduling
- Consistent, convenient software to I/O device interface through
buffering/caching, custom drivers for each device.
- File System
Built on top of disk management
- File creation/deletion.
- Support for hierarchical file systems
- Update/retrieval operations: read, write, append, seek
- Mapping of files to secondary storage
- Protection
Controlling access to the system
- Resources --- CPU cycles, memory, files, devices
- Users --- authentication, communication
- Mechanisms, not policies
- Network Management
Often built on top of file system
- TCP/IP, IPX, IPng
- Connection/Routing strategies
- ``Circuit'' management --- circuit, message, packet switching
- Communication mechanism
- Data/Process migration
- Network Services (Distributed Computing)
Built on top of networking
- Email, messaging (GroupWise)
- FTP
- gopher, www
- Distributed file systems --- NFS, AFS, LAN Manager
- Name service --- DNS, YP, NIS
- Replication --- gossip, ISIS
- Security --- kerberos
- User Interface
- Character-Oriented shell --- sh, csh, command.com ( User
replaceable)
- GUI --- X, Windows 95
Some of the Unix system calls:
(Refer to man 2.)
- Process Management
Scheduling, deadlock detection is transparent.
- fork, vfork, exit, exec
- wait
- signals, pipes, streams, sockets
- Memory management
For the most part, transparent to the user.
- malloc, free
- I/O Device Management
Devices are treated as files, so I/O devices are supported by the file
system.
- File System
- creat, open, close
- lseek, read, write
- stat, chmod, chown
- link, unlink
- mkdir, rmdir
- sync
- Hardware
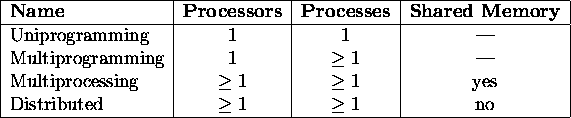
- Uniprocessor --- single CPU
- Multiprocessor --- multiple CPU's, shared memory
- Distributed system --- multiple CPU's, no shared memory (How is a
hypercube classified?)
- Software
- Process (Job, Task) --- Activity generated by a program executed
by a sequential processor. Single thread of control. Deterministic.
Is this definition bullet-proof? Can a process be associated with
more than one program? Can a program be associated to more than one
process?
- Sequential Program --- program executed by a single process
- Parallel or Concurrent Program --- program executed by several
processes
If two people run vi, does that make vi a concurrent program? What
is sharable there (this distinguishes concurrency, as does working
toward a common goal)?
- O.S. Classification
- Based on interaction with the user
- Classical --- batch, timesharing
- Special Purpose --- database, real-time
- Based on number of jobs and processors
Unix shell and commands. Foreground and background processes:
shell:
while (!EOF)
{
read cmd
parse cmd
fork cmd
if (! background command)
wait cmd
}
cmd:
execute
exit
Pipeline: c1 | c2
set up environment and pipeline
fork c1
fork c2
wait
wait
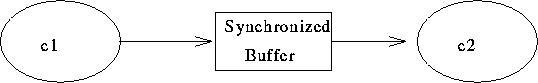
Thomas P. Kelliher
Tue Sep 10 22:31:50 EDT 1996
Tom Kelliher