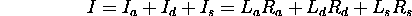Light
Tom Kelliher, CS 320
Mar. 25, 1998
Announcements:
From last time:
- 3-D maze.
Outline:
- Real world lighting.
- A lighting model.
- Shading.
- The Phong reflection model.
Assignment: Read Chapter 14.
- Viewer, lights, objects.
- Light properties?
- Material properties: Translucence, reflectance (specularity),
scattering (diffusion). Examples? Color of an object.
- How do lights and materials interact?
- The rendering equation. Calculation for each point in a scene.
- Need a balance between accuracy and efficiency.
- Local vs. global lighting. The graphics pipeline.
- General illumination function for a light source:
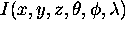 .
.
- Types of modeled light sources:
- Ambient light
- Point sources
- Spotlights
- Distant light sources
- Illumination function is a continuous function of wavelength.
- Complex computation, vision model.
- Luminance function:

- Uniform light --- ``background'' light.
- Model:

- Emits light equally in all directions.
- Assume point source at
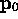 . Color vector:
. Color vector:
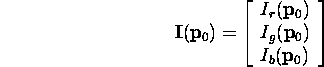
- Illumination at
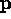 due to
due to 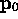 ? Depends upon square of
distance:
? Depends upon square of
distance:
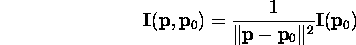
- High contrast harshness due to shadow effects: umbra, penumbra.
- In practice, replace inverse square term with

where d is the distance and a, b, and c are constants chosen to
soften.
- Simple spotlight: point source with light emitted only through narrow
range of angles.
- Consider the source at
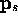 to be restricted by the cone
described by
to be restricted by the cone
described by 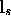 and
and 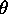 .
.
- For accuracy, distribution within the cone is modeled by
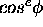 .
.
- Re-calculating the
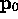 --
--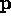 vector.
vector.
- If the distance is ``large'' how much does the vector change?
- Replace source location with source direction:
- Near source:
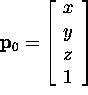 (a point)
(a point)
- Far source:
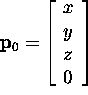 (a vector)
(a vector)
- Flat shading: each point on a polygon assigned same color.
- Gouraud (smooth) shading: assign colors individually to vertices,
interpolate.
- Consider an object point,
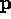 and a light source
and a light source 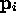 .
.
- Important vectors:
- l: vector to light source.
- n: surface normal.
- v: vector to COP.
- r: reflection vector.
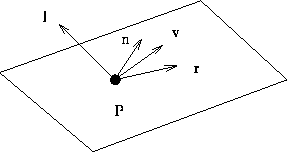
- The light from source to object can be described by:
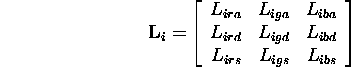
(theoretically wrong but, in practice, right)
- Using material properties, distance from source, orientation of
surface and direction of source a reflection matrix can be constructed:
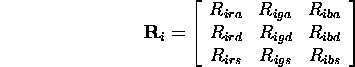
- (Simplified) Illumination at
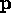 :
:
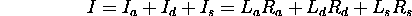
A global ambient term may be ``thrown'' in.
Thomas P. Kelliher
Tue Mar 24 14:27:34 EST 1998
Tom Kelliher
 .
.
 .
.


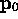 . Color vector:
. Color vector:
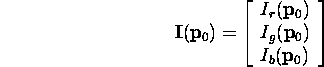
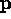 due to
due to 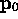 ? Depends upon square of
distance:
? Depends upon square of
distance:
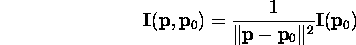

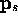 to be restricted by the cone
described by
to be restricted by the cone
described by 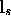 and
and 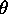 .
.
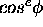 .
.
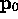 --
--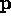 vector.
vector.
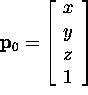 (a point)
(a point)
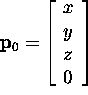 (a vector)
(a vector)
 and a light source
and a light source  .
.

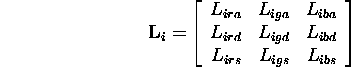
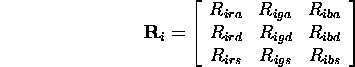
 :
: