Tom Kelliher, CS 315
Jan. 27, 1999
Read 1.1.2, 1.1.3.
Loop invariants, linear arrays, sorting on linear arrays.
Bit model, lower bounds.
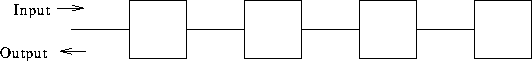
A linear array:

Cell properties:
Communication properties:
Example: sort 12, 19, 6, 15.
How many steps to sort? How many steps to output?
How can we measure a parallel algorithm? Apply following to sorting on the linear array.
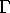 be the running time of the fastest sequential
algorithm. Then:
be the running time of the fastest sequential
algorithm. Then:

What is linear speedup?
Say you have P processors. Speedup is at most P. Why? (Hint: a parallel algorithm that runs in T steps on P processors can be simulated on a sequential machine in how many steps?)
Measures algorithm inefficiencies due to idle processors.
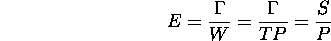
Example: consider two algorithms for solving a problem of size M:
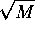 steps on an
steps on an 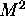 processor machine.
processor machine.
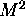 processor machine and need to run the algorithm X
times, which algorithm should we use? Assume the
processor machine and need to run the algorithm X
times, which algorithm should we use? Assume the 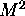 processor machine
may be split in M M processor machines.
processor machine
may be split in M M processor machines.
(Recall: 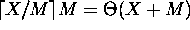 .)
.)
Let's say we want to solve a problem of size N with P processors.
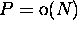 fine-grain processors in a
linear array. Can we sort N numbers?
fine-grain processors in a
linear array. Can we sort N numbers?
Fine-grain vs. coarse-grain processing.

What about simulating 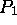 processors on
processors on 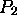 processors, where
processors, where 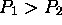 ?
?
What slowdown do we encounter?
Implications: