Tom Kelliher, CS23
Mar. 19, 1996
Guessing at a solution and backing up out of a deadend.
Place 4 Queens on a 4 by 4 chess board such that no Queen can be attacked by another.
What's recursive about this?
Try it.
Pseudocode:
int place(int column)
{
int row = 1;
if (column > 4)
return success;
while (row < 5)
{
if safe(row, column) // check that no attacks can occur
{
place queen at board[row][column];
if (place(column + 1) == success)
return success;
pick up queen at board[row][column];
}
++row;
}
return failure;
}
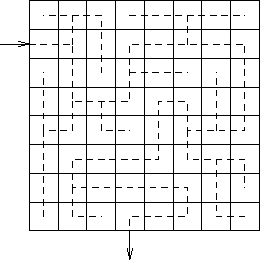
How would you find a route through the maze?

Representation of the maze?
Pseudocode:
int search(block)
{
mark block "path";
if block is goal
return success;
if block to north exists and is unvisited
if (search(block to north) == success)
return success;
if block to east exists and is unvisited
if (search(block to east) == success)
return success;
if block to south exists and is unvisited
if (search(block to south) == success)
return success;
if block to west exists and is unvisited
if (search(block to west) == success)
return success;
mark block "no path";
return failure;
}
A language is a set of strings of symbols. The C++ language is the set of strings of symbols accepted by a C++ compiler.
A grammar is a set of rules describing a language. The rules tell you how to build a string belonging to the language.
Consider a simple grammar:
<expr>=<term>{+|-<term>}
<term>=<factor>{*|/<factor>}
<factor>=(<expr>)|<letter>
<letter>=a|b|c|...|z
What language is described?
Extended Backus-Naur Form (EBNF):
Expressing associativity, precedence?
Construct the derivation, parse tree, and evaluation tree for:
(a + b) * (c + d)
a + b * c + d
(a + b) * c + d
a + b * (c + d)
Relationship between a production and a recursive set of functions?
/**********************************************************************
* expr.cc --- Convert infix expression to postfix form and indicate
* if the infix expression was properly formed.
*
* This is a recursive descent parser, implementing the following
* grammar:
* <expr>=<term>{+|-<term>}
* <term>=<factor>{*|/<factor}
* <factor>=(<expr>)|<letter>
* <letter>=a|b|c|...|z
**********************************************************************/
#include <iostream.h>
#include <ctype.h>
void GetToken(void);
int Expression(void);
int Term(void);
int Factor(void);
char Token; // Next character in the input stream --- one character
// lookahead.
/**********************************************************************
* main()
**********************************************************************/
int main()
{
cout << "Type return on an otherwise empty line to exit.\n\n";
while (1)
{
cout << "Expression: "; // Read infix expression.
GetToken();
if (Token == '\n') //
return 0;
// Parse the expression; if successful and we've read the entire line,
// then we saw a valid expression
if (Expression() && Token == '\n')
cout << "\nValid expression\n";
else
{
cout << "\nInvalid expression\n";
while (Token != '\n') // finish off the line
GetToken();
}
}
return 0;
}
/**********************************************************************
* Expression() --- Parse an expression
* This implements the production <expr>=<term>{+|-<term>}
**********************************************************************/
int Expression(void)
{
char Operator;
if (!Term())
return 0;
while (Token == '+' || Token == '-')
{
Operator = Token;
GetToken(); // Remove operator from input stream.
if (!Term())
return 0;
cout << Operator; // The operator is output following the
// operands --- converting the expression
// to postfix.
}
return 1;
}
/**********************************************************************
* Term() --- Parse an term
* This implements the production <term>=<factor>{*|/<factor>}
**********************************************************************/
int Term(void)
{
char Operator;
if (!Factor())
return 0;
while (Token == '*' || Token == '/')
{
Operator = Token;
GetToken(); // Remove operator from input stream.
if (!Factor())
return 0;
cout << Operator; // Postfix formulation.
}
return 1;
}
/**********************************************************************
* Factor() --- Parse an factor
* This implements the productions <factor>=(<expr>)|<letter>
* and <letter>=a|b|c|...|z
**********************************************************************/
int Factor(void)
{
if (islower(Token))
{
cout << Token; // Operands output immediately
GetToken(); // Remove operand from input stream.
return 1;
}
else if (Token == '(')
{
GetToken(); // Remove '(' from input stream.
if (Expression() && Token == ')') // check for parenthesized
// expression
{
GetToken(); // Remove ')' from input stream.
return 1;
}
else return 0;
}
else
return 0;
}
/**********************************************************************
* GetToken() --- read the next token from cin into the global variable
* Token.
**********************************************************************/
void GetToken(void)
{
cin.get(Token);
}
Actions associated with each production?
Could we evaluate expressions?
Could we add an assignment operator?