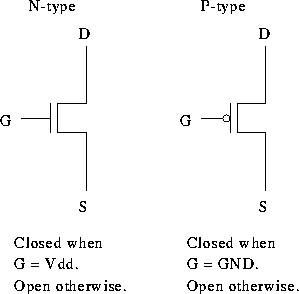
Tom Kelliher, CS 220
Oct. 20, 1997
Any questions on the homework?
Outline:
Read Intel white paper for next time.
Diagrams:

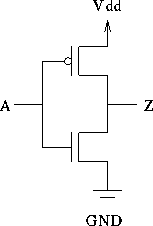
A CMOS inverter:
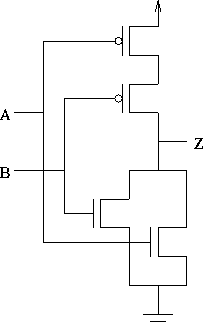
A CMOS 2-input NOR gate:
What determines power dissipation?
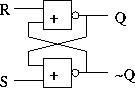
An RS latch:
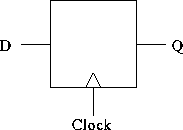
A D flip-flop:
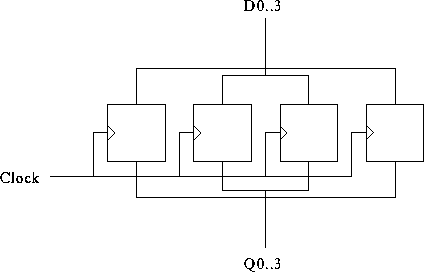
A four-bit register:
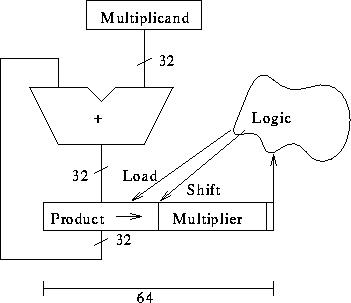
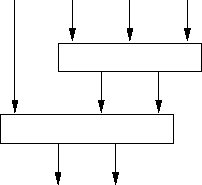
Block diagram:
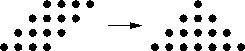
Consider the partial product matrix for four-bit multiplication:
Consider the effects of carry-save adders:
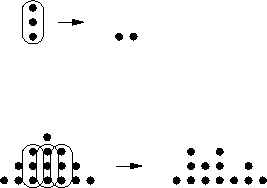
Continue this. How many levels?
But, this differs from:
Tradeoff: minimize number of CSAs or minimize time.
Tradeoff: speed of Wallace tree vs. speed of shift accumulate.