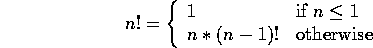
Tom Kelliher, CS18
Feb. 23, 1996
What is it?
A function that calls itself directly or indirectly to solve a smaller version of its task until a final call which does not require a self-call is a recursive function.
Divide and conquer approach
What do I need?
Looking up a word in the dictionary?
Algorithm:
Search(dictionary)
{
if (Dictionary has only 1 page)
Sequentially search page for word
else
{
Open the dictionary to the middle page
Determine which half of the dictionary the word is in
if (The word is in the first half)
Search(first half of dictionary) // ignore second half
else
Search(second half of dictionary // ignore first half
}
}
Dictionary structure?
Compare to sequential search
Meet requirements?
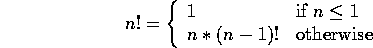
Consider the code fragment:
main()
{
int i = 3; // 1
cout << f(i) << endl; // 2
}
int f(int a1)
{
if (a1 <= 1) // 3
return 1; // 4
else // 5
return a1 * f(a1 - 1); // 6
}
Non-recursive version:
int fact(int n)
{
int i;
int prod = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
prod *= i;
return prod;
}
Definition:

Consider:
int fib(int val)
{
if (val <= 2)
return 1;
else
return fib(val - 1) + fib(val - 2);
}
Call graph for fib(6):
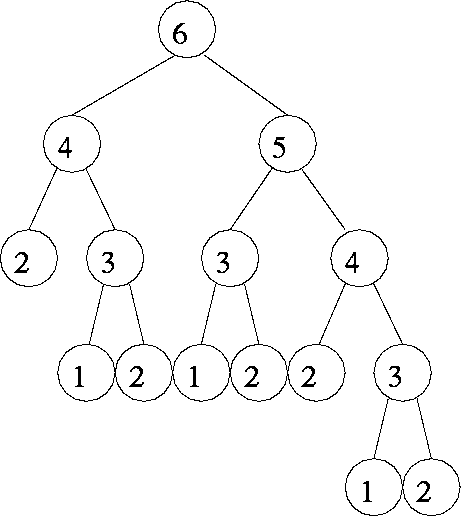
Non-recursive version:
int fib(int val)
{
int current = 1;
int old = 1;
int older = 1;
val -=2;
while (val > 0)
{
current = old + older;
older = old;
old = current;
--val;
}
return current;
}
Definition:
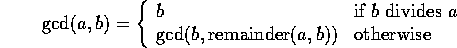
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
int remainder = a % b;
if (remaider == 0)
return b;
else
return gcd(b, remainder);
}
What does this do?
int main()
{
int array[4] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
mystery(array, 4);
}
void mystery(int array[], int size)
{
if (size > 0)
{
--size;
cout << array[size] << endl;
mystery(array, size);
}
}
How about this?
int mystery(int array[], int size)
{
--size;
if (size > 0)
return a[size] + mystery(array, size);
else
return a[size];
}
Write a recursive function which finds the maximum value stored in an int array.