Databases
Tom Kelliher, CS14F
Oct. 29, 1996
What is a database? Organized collection of information.
What are operations associated with a database?
- Store information.
- Organize information.
- Retrieve information.
Two types of databases:
- File management system --- single file.
- Database management system --- multiple files, relationships between
files.
How would an individual use a database?
How would an organization use a database?
Is the World Wide Web a database?
What are the impacts upon society?
- File --- Usually a binary file in a proprietary format. Contains
records.
- Record --- Information about one ``entity.'' Contains fields.
- Field --- One ``bit'' of information about an entity.
Abstract view of a database:
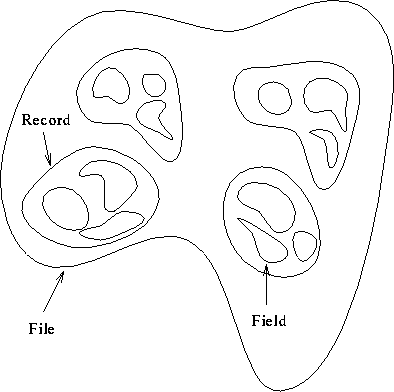
Note: each record has same number of fields.
Catalog of CDs:
- One record for each CD.
- Fields:
- Title.
- Artist.
- Year.
- Type (alternative, classical, jazz, etc.)
- Label.
- Track number.
- Track title.
- Order number.
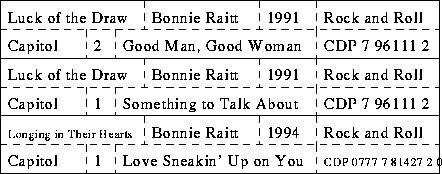
Can we put all the track titles into one record?
- Flat file systems.
- Single file databases.
- No linking to other files.
- Only one ``view.''
- Redundancy (consider CD example).
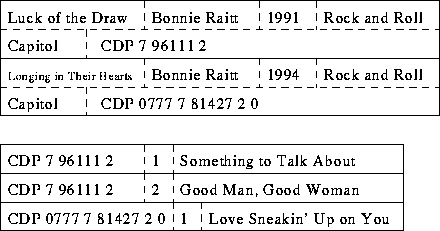
- Relational database.
- Multiple files.
- Relationships between files.
- Relational model:
- Entity.
- Relationship.
- Key field (sometimes multiple fields).
- Redundancy elimination. Why is redundancy bad?
- Data Definition Language.
- Data Manipulation Language.
- Query Language (SQL).
- Report Generator.
Thomas P. Kelliher
Sun Oct 27 18:23:42 EST 1996
Tom Kelliher



