Web Page Design Principles
Tom Kelliher, CS 102
Feb. 23, 1998
Announcements: Quiz on Friday. Will cover password selection, privacy
discussions of 2/18 and Web design principles (today's material, most of
which is taken from Chapter 3 of FrontPage text.).
From last time:
- Published web pages.
Outline:
- Web design principles.
- Properties of images/GUI systems.
Assignment:
The following are links to sites where you can get background images,
buttons, bullets, horizontal rules, etc.
-
http://www.microsoft.com/gallery/default.asp
--- Microsoft's SiteBuilder
Gallery.
-
http://home.netscape.com/assist/net_sites/starter/samples/index.html
--- Netscape Navigator Gold Tool Chest.
-
http://www.coolnerds.com/webart.htm
--- Coolnerds Web Art.
-
http://www.meat.com/textures/
--- Texture Land.
-
http://www.clipart.co.uk/
--- Clip Art Warehouse.
It's also fairly easy to find additional sites via search engines.
- The Web is a nonlinear, hypermedia, multimedia experience.
- The viewer is ultimately the author.
- Default colors for background, text, links, font size.
- Resolution, color depth?
- Viewer controls size of browser window.
- Multitude of browsers; some are text-only.
- Little control over element placement.
- Storyboard --- sketch out the design of your site and how
everything fits together.
- Make the structure intuitive.
- Design for widest possible audience and manage bandwidth:
- Keep in mind the lowest common denominator: 256 colors,
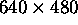 resolution.
resolution.
- Each page should download quickly for a 28.8 KB modem. Multimedia
eats bandwidth. Text doesn't.
- Keep pages short --- better to have lots of linked small pages then
one huge page.
- Provide navigation aids: back, home buttons or a table of contents in
a frame.
- Use descriptive titles.
- Provide navigation aids.
- Use image captions ( Alternate Representation in Image
Properties).
- Check spelling.
- Apply a style consistently.
- Use tables to gain structure within a page.
- Identify yourself, give contact information, and date your pages.
- Use color, motion appropriately.
- Apply the site evaluation rules to your own site.
- Overwhelm the viewer with too much.
- Use under-construction signs.
- Use images that don't fit into
 .
.
- Leave contact information.
- Ramble.
- Use broken links.
- Pixels.
- Common resolutions:
- 640 x 480.
- 800 x 600.
- 1024 x 768.
- Image size.
- How much is visible to a viewer, without scrolling?
- Formats:
- GIF --- interlaced, non-interlaced. Limited to color depth of
256. Compression controversy.
- JPEG --- Joint Photographs Expert Group. Higher color depths.
- Color depth. Common values:
- 2 --- black and white.
- 16 --- simple artwork.
- 256 --- more complex artwork, photographs.
- 32K and higher --- photographs and JPEG.
- Size of the image file. Time to load.
- In-line and external images.
- Thumbnail images.
- Copyrights.
Thomas P. Kelliher
Sun Feb 22 16:49:25 EST 1998
Tom Kelliher
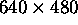 resolution.
resolution.
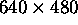 resolution.
resolution.
 .
.